HOME > Project > Laboratory of Biomembrane
Laboratory of Biomembrane

Laboratory Head
Kohji Kasahara
Laboratory of Biomembrane
Brochure 2018_PDF ![]() (136.9KB)
(136.9KB)
Backgrounds
Physiological Functions of Lipid Rafts /
Glycosphingolipid Microdomains in
Transmembrane Signaling
Lipid rafts are dynamic assemblies of glycosphingolipids, sphingomy-elin, cholesterol, and proteins that can be stabilized into microdomains in volved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes.
We have been investigating the association of glycosphingolipids with specific proteins in the nervous system and blood platelets.
We demonstrated that anti-ganglioside GD3 antibody co-precipitates GPI-anchored neural cell adhesion molecule TAG-1, src-family kinase Lyn, its substrate Cbp, trimeric G protein Goα of cerebellar granule cells.
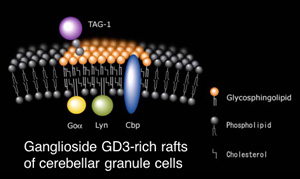
TAG-1 plays roles in axonal guidance, and cellular migration. GPI anchors have no direct contact with the cyto-plasm. We demonstrated that TAG-1 transduces signal viaLyn/Cbp in ganglioside GD3-rich rafts of cerebellar granule cells. Chemokine SDF-1α triggers the chemoattraction of cerebellar granule cells during cerebellar development.
We demonstrated that SDF-1α stimulates GTPγS binding to Goα, and causes Goα translocation to lipid rafts, leading to growth cone collapse of cerebellar granule cells.
“We found that glycosphingolipids function as platforms in transmembrane signaling for the attachment of various signaling molecules of neurons and platelets.”
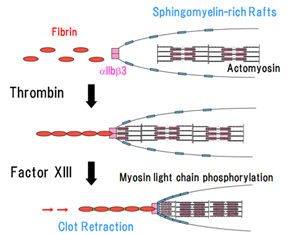
Sphingomyelin-rich rafts of platelets
Fibrin associates with lipid rafts on the platelets and raft integrity is required for clot retraction. We propose that clot retraction is mediated by factor XIII-dependent fibrin-integrin αIIbβ3-myosin axis in sphingomyelin-rich membrane rafts.
Member
Laboratory Head Kohji Kasahara
- Tetsuya Hirabayashi
- Kiyoshi Ogura