Nrf1 maintains proteasome activity but is rapidly degraded under normal condition. Upon proteasome dysfunction, Nrf1 undergoes “sequence editing” by NGLY1, converting glycosylated asparagine to aspartic acid. This study identifies the precise regulatory mechanism where edited Nrf1 recruits HCFC1-OGT and CBP/p300 complexes for gene activation. Crucially, the researchers found that while Nrf1 is essential for proteasome activation, its continuous activation is toxic, highlighting the vital importance of its transient, precise regulation.

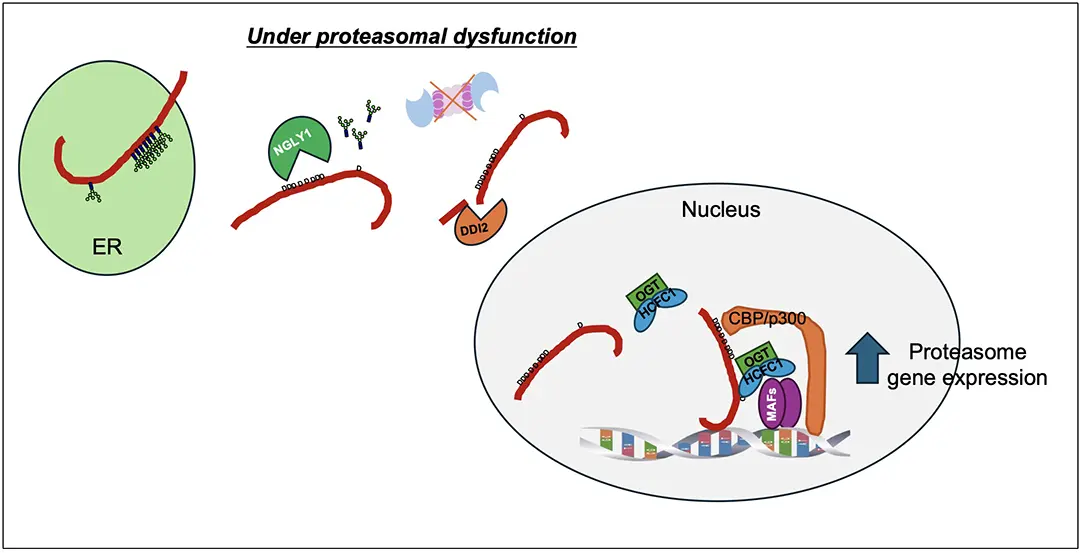
The proteasome is critical “waste disposal” system for cellular homeostasis. The transcription factor Nrf1 acts as a central sensor, activating proteasome genes when proteasomal activity is compromised.
Nrf1 is a short-lived protein. It is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and immediately glycosylated. Under normal conditions, Nrf1 is rapidly degraded via the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. When proteasome function declines, however, Nrf1 escapes degradation, undergoes activation in the cytosol, and translocates to the nucleus to induce gene expression..
A key step in this activation is “sequence editing” by NGLY1. This process removes sugar chains and converts glycosylated asparagine (N) to asparagine (D). Our study identified the complete set of genes regulated by this edited Nrf1 and demonstrated that this editing is essential for proteasome gene induction.
Nrf1 undergoes nine glycosylation events during synthesis in the ER. Our findings reveal that editing at the ninth site is particularly critical, as it creates a binding site for the nuclear protein HCFC1. This interaction, facilitated by and HCFC1-OGT dimer, ensures Nrf1 is retained in the nucleus and binds effectively to chromosomes. We also found that sequence editing at other sites enables Nrf1 to interact with CBP and p300, which activate transcription. These interactions are necessary for Nrf1 to fully tune on its target genes.
Importantly, we observed that continuous activation of Nrf1 is detrimental. Cells expressing a constitutively activate form of Nrf1 showed increased proteasome activity but ultimately underwent cell death. In contrast, naturally edited form of Nrf1 transiently activates a broad range of genes, including proteasome components, stress-resistant factors, autophagy-related factors, anti-inflammatory factors, and inflammatory cytokines. These suggests that temporary activation of Nrf1- occurring only when strictly necessary - is a sophisticated survival strategy.
In summary, Nrf1 must be regulated with exceptional precision. Synthesized as a glycoprotein in the ER, where it is constantly subject to degradation. It functions in the nucleus only when required, following a strict two-step activation mechanism involving cleavage by DDI2 and amino acid editing by NGLY1.