HOME > Topics2019 > 26 August 2019
26 August 2019
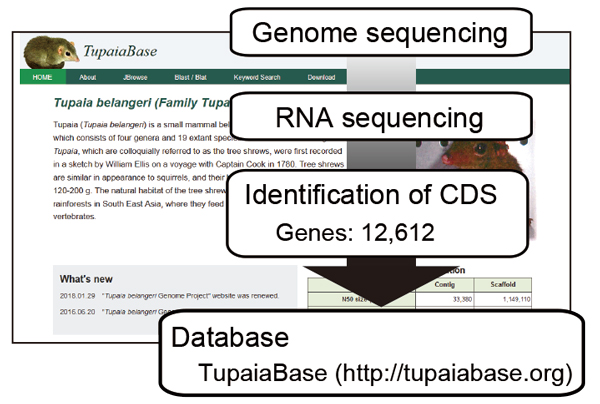
Takahiro Sanada (Viral Infectious Diseases Project) published a paper on “Construction of complete Tupaia belangeri transcriptome database by whole-genome and comprehensive RNA sequencing” in Scientific Reports
Construction of complete Tupaia belangeri transcriptome database by whole-genome and comprehensive RNA sequencing
- <Title of the paper>
- Construction of complete Tupaia belangeri transcriptome database by whole-genome and comprehensive RNA sequencing
- <Journal>
- Scientific Reports
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-48867-x
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48867-x
Summary
The northern tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri ) possesses high potential as an animal model of human diseases and biology, given its genetic similarity to primates. Although genetic information on the tree shrew has already been published, some of the entire coding sequences (CDSs) of tree shrew genes remained incomplete, and the reliability of these CDSs remained difficult to determine. The improvement of the determination of tree shrew CDSs was required.
In collaboration with Kagoshima University, BITS Co., Ltd., National Institute of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition, National Institute of Genetics, and National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Dr. Takahiro Sanada (Viral infectious diseases project) and his colleagues in Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science performed sequencing of the whole-genome, mRNA, and total RNA and integrated the resulting data. Additionally, the researchers established criteria for the selection of reliable CDSs and annotated these sequences by comparison to the human transcriptome, resulting in the identification of complete CDSs for 12,612 tree shrew genes and yielding a more accurate tree shrew genome database (TupaiaBase: http://tupaiabase.org). Transcriptome profiles in hepatitis B virus infected tree shrew livers were analyzed for validation. Gene ontology analysis showed enriched transcriptional regulation at 1 day post-infection, namely in the “type I interferon signaling pathway”. Moreover, a negative regulator of type I interferon, SOCS3, was induced.
This work, which provides a tree shrew CDS database based on genomic DNA and RNA sequencing, is expected to serve as a powerful tool for further development of the tree shrew model.