- HOME
- Dementia Research Project
Dementia Research Project
Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms of dementia and the development of novel treatments and preventive methods
Achievements in 2024
In 2024, we found that tau from a patient with a VCP D395G mutation contained CTE (chronic traumatic encephalopathy)-type folds instead of AD-type folds. We also analyzed TDP-43 filaments from a patient with FTLD-TDP type C and found that TDP-43 forms heteromeric filaments with a second protein, ANXA11. Previously pathological proteins were only known to form homomeric filaments. These studies show that the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases is much more varied and complex than previously thought.
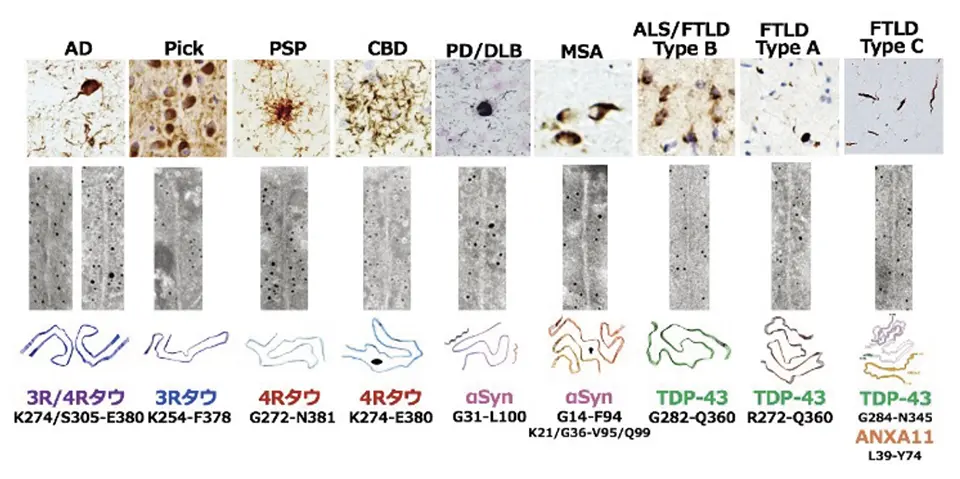
Publications
Papers in 2024
- Arseni D, Nonaka T, et al. (2024) “Heteromeric amyloid filaments of ANXA11 and TDP-43 in FTLD-TDP Type C”. Nature. 634(8034):662-668.
- Qi C, et al. (2024) “Tau filaments with the chronic traumatic encephalopathy fold in a case of vacuolar tauopathy with VCP mutation D395G”. Acta Neuropathol. 147(1):86.
- Kametani F, et al. (2024) “Analysis and comparison of post-translational modifications of α-synuclein filaments in multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies”. Sci Rep. 14(1): 22892 .
Key papers
- Qi C, et al. (2023) “Tau filaments from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex adopt the CTE fold”. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 120(51): e2306767120.
- Tarutani A, et al. (2023) “Distinct tau folds initiate templated seeding and alter the post-translational modification profile”. Brain 146(12):4988-4999.
- Arseni D, et al. (2023) “TDP-43 forms amyloid filaments with a distinct fold in type A FTLD-TDP.” Nature. 620(7975):898-903.
- Yang Y, et al. (2022) “Structures of α-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology”. Nature. 610(7933):791-795.
- Schweighauser M, et al. (2022) “Age-dependent formation of TMEM106B amyloid filaments in human brains”. Nature. 605(7909):310-3148.
- Arseni D, Hasegawa M, et al. (2022) “Structures of TDP-43 filaments from amyotrophic 1 lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal lobar degeneration”. Nature. 601(7891):139-143.
- Hosokawa M, et al. (2022) “Development of a novel tau propagation mouse model endogenously expressing 3 and 4 repeat tau isoforms.” Brain. 145(1):349-361.
- Tarutani A, et al. (2021) “Human tauopathy-derived tau strains determine the substrates recruited for templated amplification.” Brain. 144(8):2333-2348.
- Shi Y, et al. (2021) “Structure-based classification of tauopathies.” Nature. 598(7880):359-363.
