- HOME
- Child Brain Project
Child Brain Project
A Consortium to Overcome Childhood Brain Diseases
Achievements in 2024
Chronic stressful environments are known to induce depressive and anxiety-like behaviors in mice. We demonstrated that chronic stress conditions induce depressive and anxiety-like behaviors by decreasing the expression of Neuritin, which in turn suppresses the activation of FGF signaling and reduces axonal branching of serotonergic neurons.
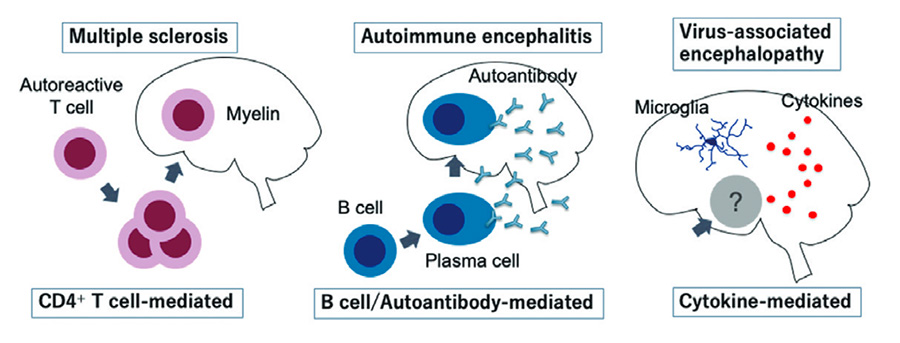
In clinical research, as a result of our multi-institutional clinical studies, we developed a diagnostic prediction score for NMDAR encephalitis in children and clarified the clinical characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 associated encephalopathy. We also led an international collaborative study on virus-related acute encephalopathy that proposed the new concept of infection-triggered encephalopathy syndrome (ITES) and published consensus guidelines for it.
Publications
Papers in 2024
- Shimada T, et al. (2024) “ Neuritin controls axonal branching in serotonin neurons: A possible mediator involved in the regulation of depressive and anxiety behaviors via FGF signaling. ” J Neurosci. 44: 1-17.
- Kasai M, et al. (2024) “ Clinical characteristics of SARS-CoV-2-associated encephalopathy in children: Nationwide epidemiological study. ” J Neurol Sci. 457:122867.
- Sakuma H, et al. (2024) “ International consensus definitions for infection-triggered encepha- lopathy syndromes. ” Dev Med Child Neurol. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.16067.
Key papers
- Nosadini M et al. (2021) “Use and safety of immunotherapeutic management of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibody encephalitis: a meta-analysis.” JAMA Neurol. 78:1333-1344.
- Horino A, et al. (2021) “Intrathecal dexamethasone therapy for febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome.” Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol, 8:645-655.
- Nishida H et al. (2021) “Evaluation of the diagnostic criteria for anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in Japanese children.”Neurology. 50:e2070-e2077.
